Controlling Access to Management Portal Functions
This page describes how the Management Portal uses the predefined security roles and resources to control access to pages and options related to production management.
InterSystems recommends that you do not modify predefined roles. Rather, create a new role based on the predefined role and modify the role that you have created.
Introduction
InterSystems IRIS® data platform contains predefined roles which you can use to control access to the functions in the Management Portal. While these built-in roles may suit most environments, you can add additional roles to customize access to pages or functions.
The following sections describe the security structure prebuilt in InterSystems IRIS. You can use this information to determine how to assign your users to roles in your environment.
For an overview of InterSystems security, see About InterSystems Security, and in particular, Authorization: Controlling User Access
Predefined Resources
This section describes the predefined resources related to productions. The names of these resources all begin with the %Ens_ prefix.
-
The first subsection lists resources that protect a specific activity you can perform in InterSystems IRIS.
-
The second subsection lists code and data resources.
You can view the list of predefined resources on the System Administration > Security > Resources page of the Management Portal.
For an in-depth discussion of resources, see Assets and Resources.
Resources to Protect Activities Related to Productions
Controls access to managed alert administration.
Controls starting and stopping configuration items.
Controls access to the data transformation testing utility.
Controls access to the Production Monitor.
Controls access to deployment activities.
Controls the creation of deployment packages using the server.
Controls the creation and import of local deployment packages using the browser.
Controls access to the Event Log.
Controls access to the contents of messages.
Controls discarding of queued and suspended messages.
Controls access to edit and resend messages.
Controls access to export messages.
Controls access to message header data.
Controls access to resend messages.
Controls the manual suspension of messages.
Controls access to message trace.
Controls access to the Enterprise Monitor.
Controls access to the Message Bank Event Log.
Controls access to the contents of messages in the Message Bank.
Grants permission to edit and resend messages from the Message Bank.
Controls access to Message Bank header data.
Grants permission to resend messages from the Message Bank.
Controls access to the Message Bank Visual Trace.
Controls access to the Interoperability menus in the Management Portal.
To access any of the Interoperability pages and functions in the Management Portal for a given namespace, a user must also have Read permission on the default global database resource for the namespace.
Controls the creation of production documentation.
Controls starting and stopping productions.
Controls purging of production-related data.
Controls access to the Rule Log.
Controls access to the business host testing service.
Controls access to the Finder Dialog, which enables users to browse the file system.
Resources to Protect Code and Data Related to Productions
Controls access to the Agent Management page, which is applicable only to HealthShare.
Controls access to alert configuration and management.
Controls access to the Archive Manager.
Controls access to the Business Process Language (BPL).
Controls access to business rules.
Controls access to all Interoperability classes and routines.
Controls access to production credentials.
Controls access to the Data Transformation Language (DTL).
Controls access to EDI schemas.
Controls access to the HL7 Annotation classes.
Controls access to the Interoperability Toolkit, which is applicable only to HealthShare.
Controls access to Java Business Hosts.
Controls access to job data.
Controls access to lookup tables.
Controls access to Message Bank status information
Controls access to Message Bank configuration.
Controls access to the Port Authority Report, which details port usage across the system.
Controls access to production configuration activities.
Controls access to scheduling of InterSystems IRIS purge tasks.
Controls access to the Publish & Subscribe (or PubSub) pages in the Management Portal.
Controls access to the Purge Management Data page in the Management Portal and controls the default settings for manually purging production-related data.
Controls access to queue data.
If you want to perform an activity related to an active message you will also need access to job data which uses the %Ens_Jobs resource.
Restricts a user to editing only the system default settings to which they have been given USE permission. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Controls access to interoperability record maps.
Controls access to routing rules.
Controls access to all interoperability rules.
Controls access to the Setting Report Configuration page, which enables you to specify the namespace that stores data about port usage.
Controls access to system–wide default settings.
Allows user to manage the AllowedIPAddresses system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Allows user to manage the IPAddress system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Allows user to manage the LogGeneralTraceEvents system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Allows user to manage the LogTraceEvents system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Allows user to manage the Port system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Allows user to manage the Schedule system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Allows user to manage the Server system default setting even when they are restricted from managing other system default settings. For more information, see Security for System Default Settings.
Controls access to workflow roles and users.
In many cases, the default behavior uses a less granular resource (like %Ens_Code) which protects multiple data sources including the data protected by a more specific resource (like %Ens_BPL). The predefined roles and privileges use the less granular resource, but you can choose alternative roles with more selective privileges.
Security for System Default Settings
Assigning USE permission to the %Ens_RestrictedUI_SystemDefaultSettings resource restricts a user from creating, editing, or deleting system default settings for Interoperability productions. This restriction applies only to managing system default settings in the Management Portal and does not prevent administrators from editing the global directly.
You can grant exceptions to this general restriction by assigning USE privileges to the %Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_setting resource, where setting is the case-sensitive name of a setting. The system includes predefined resources as follows:
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_AllowedIPAddresses — Allows users to manage the AllowedIPAddresses setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_IPAddress — Allows users to manage the IPAddress setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_LogGeneralTraceEvents — Allows users to manage the LogGeneralTraceEvents setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_LogTraceEvents — Allows users to manage the LogTraceEvents setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_Port — Allows users to manage the Port setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_Schedule — Allows users to manage the Schedule setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
-
%Ens_SystemDefaultSettings_Server — Allows users to manage the Server setting from the Management Portal even when blocked from managing other system default settings.
For more information about system default settings, see Defining System Default Settings. For instructions on creating resources, see Create or Edit a Resource.
Predefined Roles Related to Productions
InterSystems IRIS also contains a set of predefined roles related to productions. Their names each begin with the %EnsRole_ prefix. These are roles designed to reasonably secure your InterSystems IRIS instances in both development and live environments. The following descriptions contain an overview of the perceived job responsibilities of members of the role and how these roles relate to other roles.
To make a custom role that mimics the functionality of a predefined role, you must give the custom role all the privileges that the original predefined role had. This includes both its resource privileges and SQL privileges (System > Security Management > Roles > Edit Role).
Excluding these SQL privileges can cause the following error:
ERROR #5540: SQLCODE: -99 Message: User is not privileged for the operation
Role for a trusted and skilled administrator. In a live or test system this is for the person able to stop, start, and configure productions; to stop and start individual configuration items; to look at all logs, messages, and queues; to purge data; to add default system settings; and so on. This administrator has almost unlimited ability to control the InterSystems IRIS Interoperability environment, but cannot change code components other than to deploy updates.
This role is intentionally distinct from InterSystems IRIS administrative roles and does not grant the user any non-production privileges.
The %EnsRole_Administrator role is a member of the %EnsRole_Operator role, and, therefore, also holds all the privileges of that role.
Role for a person developing business logic, data structures, or core InterSystems IRIS code. This includes writing code in your IDEOpens in a new tab, writing DTL and BPL in either your IDEOpens in a new tab or the Management Portal, developing routing rules, and creating custom message schemas. In addition, this role allows a user to perform many administrative tasks, as the developer should have the ability to actively debug and test various options on development instances.
By default, members of the InterSystems IRIS Interoperability developer role have full programming power and as such, can modify DTL, BPL, and record maps. InterSystems IRIS provides separate resources for each type of code if you want to distinguish areas of development by creating custom roles.
The %EnsRole_Developer role is a member of both the %Developer and %EnsRole_WebDeveloper roles. Therefore, a user assigned to this role can perform all InterSystems IRIS development tasks as well as the web developer tasks.
Role for a person with limited development abilities. In particular, this restricts a user to the development tasks in the Interoperability menus of the Management Portal, like BPL, DTL, defining rules, and creating record maps. The role does not grant access to your IDEOpens in a new tab or the terminal.
This role is a member of the %EnsRole_RulesDeveloper and %EnsRole_Operator role, so that a user that is a member of this role can perform debugging tasks in the Management Portal.
Role for a business analyst allowed to modify business rules dynamically. If you have developed a business process that requires such a function, you can allow a small number of people to modify the rules. This is not an administrative or development function.
%EnsRole_WebDeveloper is a member of this role.
Role for a generic user to view the InterSystems IRIS system monitor and the production monitor. Actions that would leave an audit trail if done from a user with %EnsRole_Operator have no effective audit trail from this generic username and therefore access needs to be restricted to a subset that does not include any risk of seeing sensitive data.
Role for operation staff managing the day-to-day status of a particular production. Users assigned to this role have the Read permission on the current configuration to determine what settings and code are in effect, but do not have permissions to modify the configuration. Operations staff may start and stop interfaces, and may start and stop the production. They do not have access to the contents of messages, but may resend messages which cause issues. Operators may view queue and job information, and may inspect the settings for purges, alerts, credentials, and lookup tables.
Both %EnsRole_Administrator and %EnsRole_WebDeveloper are members of this role.
Role for processing managed alerts assigned to any user or unassigned. For more information on processing managed alerts, see Acting on Alerts by Viewing My Managed Alerts.
Role for processing managed alerts assigned to current user or unassigned. For more information on processing managed alerts, see Acting on Alerts by Viewing My Managed Alerts.
Role that allows user to control the subscription criteria used to select messages and to specify the users to receive the messages. This role provides access to the management portal page that controls Publish and Subscribe routing. For more information on Publish and Subscribe messages, see Defining Publish and Subscribe Message Routing.
The default InterSystems IRIS Interoperability security framework assigns permissions to the predefined resources, thus creating privileges for each of these roles. You can choose to assign the users of your application to these InterSystems IRIS Interoperability roles or create your own roles, assigning them permissions to the InterSystems IRIS resources. If you upgrade your InterSystems IRIS instance, the procedures reset the default roles, so you should make your configuration modifications only on user-created roles.
The next section shows the privileges assigned by default to each role.
You can view the list of predefined roles on the System Administration > Security > Roles page of the Management Portal.
These roles only cover functions in the Interoperability menus of the Management Portal. Users in your environment likely require additional InterSystems IRIS roles. For details, see Roles.
Roles for Business Rule Editor
The Business Rule Editor has an additional role, %EnsRole_InteropEditorsAPI, that is granted through the web application /api/interop-editors. This role does not need to be assigned to users, but will be temporarily applied when a user accesses the application. For more details on how roles and web applications work together, see Applications. Details on the resources associated with this role are provided below:
-
In order to access /api/interop-editors and obtain the %EnsRole_InteropEditorsAPI, a user must first have one of:
-
%Ens_Rules:READ
-
%Ens_BusinessRules:READ
-
%Ens_RoutingRules:READ
-
-
%EnsRole_InteropEditorsAPI grants a user %Development:USE.
-
%EnsRole_InteropEditorsAPI also grants a user EXECUTE privileges on the following SQL resources:
-
%Ens_Config.Production_Extent
-
%Studio_SourceControl.Interface_MenuItems
-
%Studio_SourceControl.Interface_MainMenus
-
%Dictionary.ClassDefinition_SubclassOf
-
%Dictionary.ClassDefinition_Summary
-
%Atlier_v1_Utils.Extension_UserAction
-
%Atlier_v1_Utils.Extension_AfterUserAction
-
%Atlier_v1_Utils.Extension_ExtensionEnabled
-
%Atlier_v1_Utils.Extension_GetStatus
-
%Atlier_v1_Utils.Extension_GetMenus
-
Default Privileges of the Predefined Roles
This section lists the default privileges that each role has for each resource.
-
The first subsection lists the role privileges for the activity resources.
-
The second subsection lists the role privileges for the code and data resources.
See Privileges and Permissions for an explanation of how you grant access to resources through role privileges.
Role Privileges for the Activity Resources
The following table lists the role privileges for the activity resources. Only the Use permission is required for access, use this permission on the underlying resource to determine access to data as well.
| Resource | %EnsRole _Administrator | %EnsRole _Developer* | %EnsRole _Monitor | %EnsRole _Operator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| %Ens_ConfigItemRun | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_DTLTest | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_Dashboard | Use | Use | Use | Use |
| %Ens_Deploy | Use | |||
| %Ens_DeploymentPkg | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_EventLog | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MessageContent | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_MessageDiscard | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_MessageEditResend | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_MessageHeader | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MessageResend | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MessageSuspend | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_MessageTrace | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MsgBank_Dashboard | Use | Use | Use | Use |
| %Ens_MsgBank_EventLog | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MsgBank_MessageContent | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_MsgBank_MessageEditResend | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_MsgBank_MessageHeader | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MsgBank_MessageResend | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_MsgBank_MessageTrace | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_Portal* | Use | Use | Use | Use |
| %Ens_ProductionDocumentation | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_ProductionRun | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_Purge | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_RuleLog* | Use | Use | Use | |
| %Ens_TestingService | Use | Use | ||
| %Ens_ViewFileSystem | Use | Use |
Role Privileges for the Code and Data Resources
The following table lists the role privileges for the code and data resources. Read and Write permissions are distinct for the resource; your application code should use these two permissions to determine access to the underlying data.
For reasons of space, this table does not include the information on all roles. Additional roles are described after the table.
| Resource | %EnsRole _Administrator | %EnsRole _Developer | %EnsRole _Monitor | %EnsRole _Operator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| %Ens_Alerts | Read, Write | Read, Write | Read | |
| %Ens_ArchiveManager | Read, Write | |||
| %Ens_BPL | ||||
| %Ens_BusinessRules | ||||
| %Ens_Code | Read | Read, Write | ||
| %Ens_Credentials | Read, Write | Read | Read | |
| %Ens_DTL | ||||
| %Ens_EDISchema | Read | Read, Write | ||
| %Ens_JBH | ||||
| %Ens_Jobs | Read, Write | Read, Write | Read | |
| %Ens_LookupTables | Read, Write | Read, Write | Read | |
| %Ens_MsgBank | Read, Write | Read | Read | |
| %Ens_MsgBankConfig | Read, Write | Read, Write | ||
| %Ens_ProductionConfig | Read, Write | Read, Write | Read | |
| %Ens_PurgeSchedule | Use | Read | Read | |
| %Ens_PurgeSettings | Read, Write | Read, Write | ||
| %Ens_Queues | Read, Write | Read, Write | Read | |
| %Ens_RecordMap | ||||
| %Ens_RoutingRules | ||||
| %Ens_Rules* | Read, Write | |||
| %Ens_SystemDefaultConfig | Read, Write | Read | Read | |
| %Ens_WorkflowConfig | Write | Read, Write | Read |
Additional roles have the following privileges
-
The %EnsRole_WebDeveloper role has the same privileges as %EnsRole_Developer, except for access to the %Ens_PurgeSettings resource.
-
The %EnsRole_RulesDeveloper role has only the following privileges:
-
%Ens_Portal:U
-
%Ens_RuleLog:U
-
%Ens_Rules:RW
-
Portal Page Privilege Requirements
Each Management Portal page has a default privilege requirement in the security framework shipped with InterSystems IRIS. You can view this requirement while in the columns view of the portal menu just beneath where you click Go to navigate to the page. You only see this information if you click next to the menu item name and not directly on the label.
For example, if you select Interoperability > Configure and then click to the right of Production on menu of the Management Portal, you see %Ens_ProductionConfig:READ listed under the System Resource(s) label. This means you must be a member of a role that has the Read permission on the %Ens_ProductionConfig resource to view the Production Configuration page.
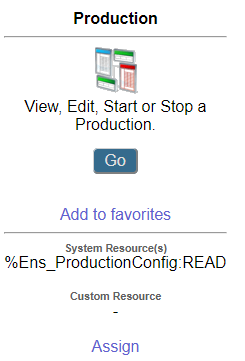
Notice you may also assign custom resources to a portal page. See Use Custom Resources with the Management Portal.
Default SQL Privileges of the Predefined Roles
Several InterSystems IRIS Interoperability pages in the Management Portal use SQL queries to retrieve information; therefore, users must have privileges on the appropriate tables to view this information. This section shows how InterSystems IRIS assigns SELECT privileges to its predefined roles to provide the proper security.
The %EnsRole_Administrator, %EnsRole_Developer, and %EnsRole_WebDeveloper roles hold the SELECT privilege on all of the following SQL tables:
-
Ens.BusinessProcess
-
Ens.BusinessProcessBPL
-
Ens.MessageBody
-
Ens.MessageHeader
-
Ens.StreamContainer
-
Ens.StringContainer
-
EnsLib_DICOM.Document
-
EnsLib_EDI_ASTM.Document
-
EnsLib_EDI_ASTM.SearchTable
-
EnsLib_EDI_EDIFACT.Document
-
EnsLib_EDI_EDIFACT.SearchTable
-
EnsLib_EDI_X12.Document
-
EnsLib_EDI_X12.SearchTable
-
EnsLib_EDI_XML.Document
-
EnsLib_EDI.XML.SearchTable
-
EnsLib_HL7.Message
-
EnsLib_HL7.SearchTable
-
EnsLib_Printing.PrintJob
-
EnsLib_Printing.PrintRequest
-
EnsLib_SQL.Snapshot
-
EnsLib_XML.SearchTable
-
EnsLib_ebXML.Message
-
EnsLib_ebXML.MessageTracking
-
EnsLib_ebXML.MessageWithPayload
-
Ens_Config.Credentials
-
Ens_Enterprise_MsgBank.Log
-
Ens_Enterprise_MsgBank.MessageHeader
-
Ens_Enterprise_MsgBank.Node
-
Ens_Rule.Log
-
Ens_Rule.RuleLog
-
Ens_Util.Calendar
-
Ens_Util.IOLog
-
Ens_Util.Log
-
Ens_Util.Schedule
The remaining roles have SELECT privileges on a subset of the SQL tables as shown in the following table.
| SQL Table Name | %EnsRole _RulesDeveloper | %EnsRole _Monitor | %EnsRole _Operator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ens.BusinessProcess | SELECT | ||
| Ens.BusinessProcessBPL | SELECT | ||
| Ens.MessageHeader | SELECT | ||
| Ens_Config.Credentials | SELECT | ||
| Ens_Enterprise_MsgBank.Log | SELECT | ||
| Ens_Enterprise_MsgBank.MessageHeader | SELECT | ||
| Ens_Enterprise_MsgBank.Node | SELECT | ||
| Ens_Rule.Log | SELECT | SELECT | |
| Ens_Rule.RuleLog | SELECT | SELECT | |
| Ens_Util.Calendar | SELECT | ||
| Ens_Util.Log | SELECT | SELECT | |
| Ens_Util.Schedule | SELECT |
InterSystems IRIS also grants privileges on two stored procedures:
-
EXECUTE privileges on the Ens_Config.Production_Extent stored procedure (used by the system to list and load productions) to %EnsRole_Administrator and %EnsRole_Developer
-
EXECUTE privileges on the Ens.IsASub stored procedure (used by the system in certain searches of the Message Viewer) to %EnsRole_Administrator, %EnsRole_Developer, and %EnsRole_WebDeveloper
If you define a custom role and want a user with the role to be able to perform searches on messages, you should grant EXECUTE privileges on the Ens.IsASub to the role or user. To see if a specific role has this privilege in an interoperability-enabled namespace:
-
Select System Administration, Security, and Roles.
-
Select the role.
-
Select the SQL Procedures tab.
-
Select the namespace from the drop-down menu.
If the role has the Ens.IsASub privilege, Ens.IsASub is listed and marked as having EXECUTE privilege. If the role does not have this privilege in the namespace, you can give it this privilege by doing the following on the SQL Procedures tab:
-
Click the Add Procedures ... button.
-
Select the Ens schema from the drop-down menu.
-
Select IsASub from the Available column.
-
Click the right arrow to add IsASub to the Selected column.
-
Click Apply and then Close.
You can also give this SQL procedure privilege directly to a user.
InterSystems IRIS automatically grants permissions to allow the specified roles to run SELECT statements as described in the previous tables. It grants these permissions for the tables generated for the built-in message types. If you define custom message types, you should grant the same permissions to these roles for the tables generated for these custom message types.
Customizing Security
For information on customizing security, see the following topics: